A Graph Neural Network Model Enables Accurate Prediction of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors Compared to Other Machine Learning Models
Abstract
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), a tyrosine kinase receptor, is identified as a crucial target in the progression of anticancer therapeutics for non-small cell lung cancer. This study has executed a Graph Neural Network (GNN) model and compared it with three machine learning (ML) models based on fingerprints for rapid anticancer bioactivity prediction. ALK inhibitors with IC50 values were extracted from the REAXYS database. Following preprocessing, these inhibitors constituted a dataset of 1664 molecules. Subsequently, GNN and ML models were constructed on a training set. The generalizability of these models was assessed by internal and external validation procedures. The graph neural network model yielded promising results, with an average precision of 0.879±0.041 and an F1 score of 0.804±0.049 in cross-validation. In external validation, the model achieved an average precision of 0.938 and an F1 score of 0.863, surpassing the results of the ML models. Therefore, we can infer that the predictive model developed using the GNN is apt for the problem at hand and can be utilized to predict the biological activity of novel ALK inhibitors.
Workflow
- Network structure
- The proposed GNN model obtained graph data as the input and used multiple TransformerConv, linear, and batch normalization layers to embed the graph representation. TopKPooling layers reduced the graph size by selecting the top k crucial nodes. The global representation was obtained by aggregating intermediate representations and passing them through three linear layers to produce a single output value.
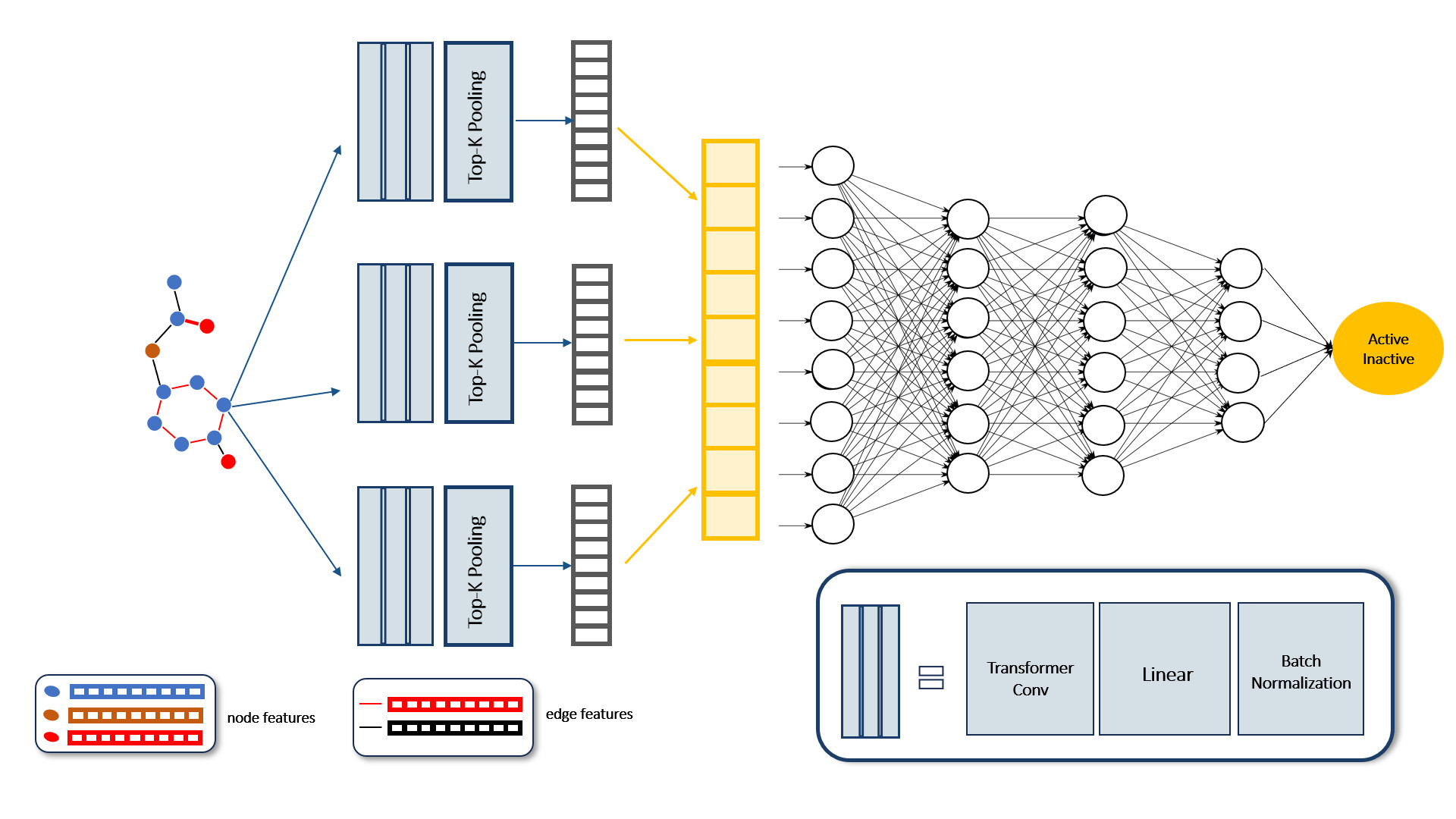
- The proposed GNN model obtained graph data as the input and used multiple TransformerConv, linear, and batch normalization layers to embed the graph representation. TopKPooling layers reduced the graph size by selecting the top k crucial nodes. The global representation was obtained by aggregating intermediate representations and passing them through three linear layers to produce a single output value.
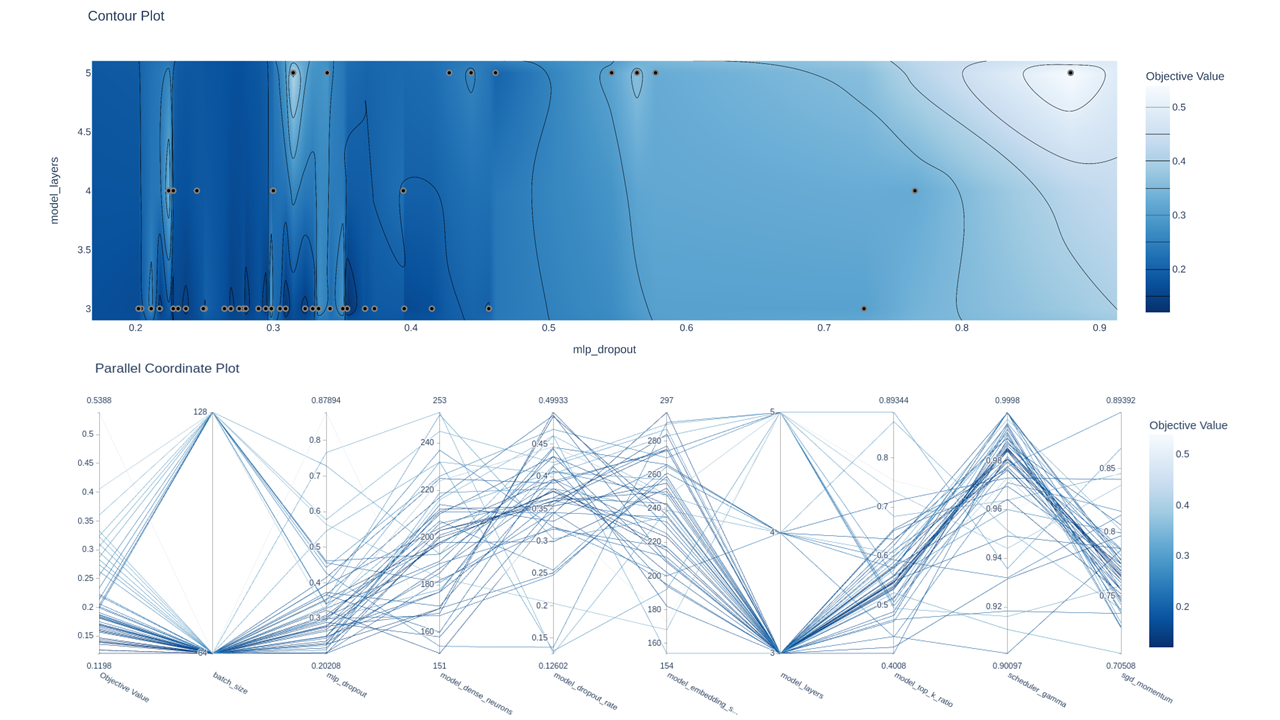
- Hyperparameter tunning
- Ensemble Graph neural network
- To mitigate this uncertainty issue, we constructed an ensemble model, referred to as E-GNN, using the soft-voting method. This method entailed independently training 30 ‘sub’ GNN models with similar hyperparameters as those discovered form hyperparameter tunning phase and making predictions for a given data point utilizing all 30 models. The process of constructing the ensemble model is illustrated in below figure.
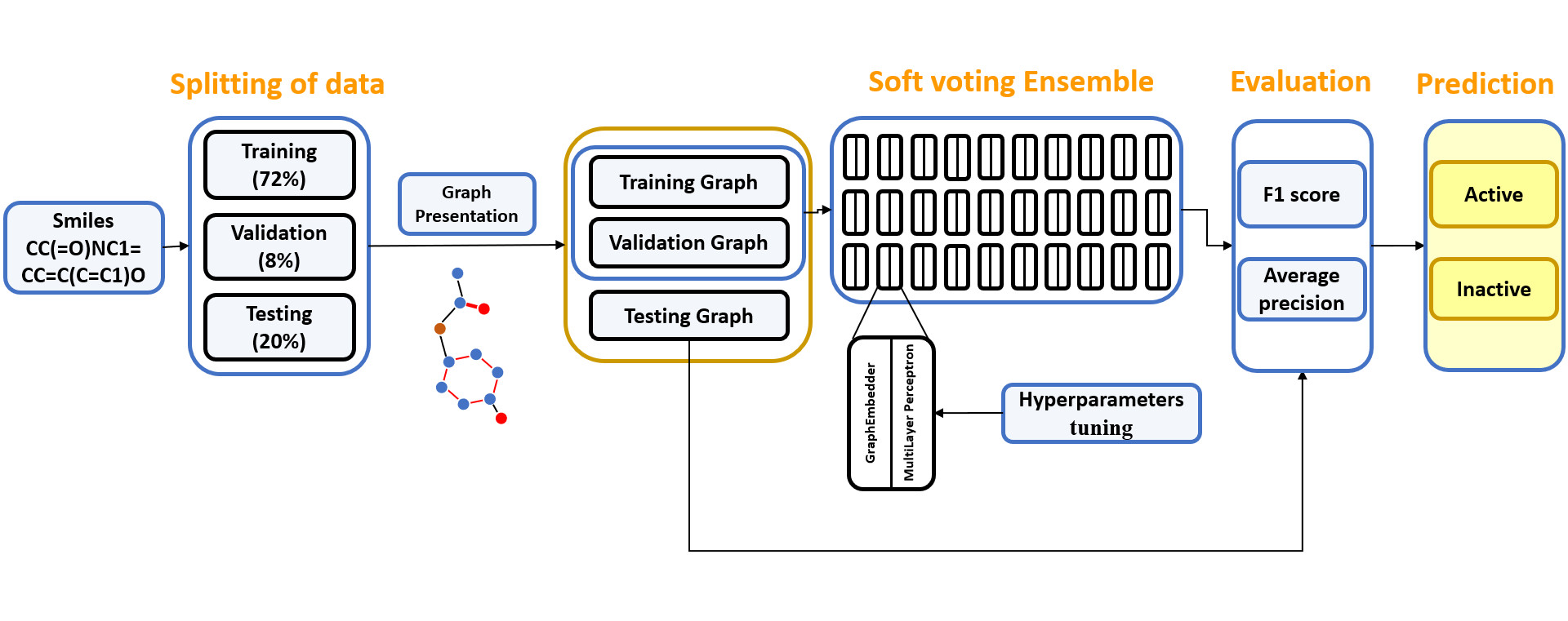
- To mitigate this uncertainty issue, we constructed an ensemble model, referred to as E-GNN, using the soft-voting method. This method entailed independently training 30 ‘sub’ GNN models with similar hyperparameters as those discovered form hyperparameter tunning phase and making predictions for a given data point utilizing all 30 models. The process of constructing the ensemble model is illustrated in below figure.
Publication manuscript.
For more detailed information, please access to Proceeding of IEEE to see the paper here. 
Requirements
This module requires the following modules:
Contributing
Please visit repository of this publications.